A drug that was supposed to help people get off heroin has "created a new cash-for-pills market and a street trade" that state officials are trying to stop, Mary Meehan reports for the Lexington Herald-Leader.
The drug is buprenorphine, the active ingredient in the brand-name drugs Suboxone and Subutex, which became more popular in 2012, when the state cracked down on "pill mills" that were freely handing out prescriptions for painkillers. "A lot of the pill mills morphed into facilities that dispense these prescriptions," Dr. John Langefeld, medical director for the state's Medicaid program, told Meehan.
Also, Meehan writes, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act required insurance plans to cover treatment for substance abuse, and "as more Medicaid patients and others got health-insurance coverage, more people obtained prescriptions for buprenorphine, Langefeld said. . . . According to a state report, one user obtained prescriptions from nine doctors."
Use of the drug in Kentucky "has increased 241 percent since 2012," Meehan reports. "And 80 percent of the prescriptions for it were being written by 20 percent of the state's 470 certified prescribers, said Dr. Allen Brenzel, medical director of the state's Department of Behavioral Health. . . . Since 2011, 10 doctors have been sanctioned by the Kentucky Board of Medical Licensure because of problems prescribing Suboxone."
Suboxone is supposed to be taken in conjunction with therapy and drug testing. "a patient receives a controlled dose of a legal drug as the dose is tapered by a physician for a safe and effective withdrawal," Meehan notes. However, "doctors started to see Suboxone patients on a cash basis, asking for as much as $300 for an office visit that included a prescription for the maximum allowable amount of Suboxone. Patients often received no therapy or drug testing. Some patients were on the maximum dose indefinitely, Brenzel said." Some doctors prescribed the drug with other painkillers, creating an illegal market.
To prevent such abuse by unscrupulous doctors, the medical-licensure board has issued regulations that require "more physician education and the requirement that the drug be prescribed only for medically supervised withdrawal and not be given to pregnant women," Meehan writes. "Patients should also be closely monitored and drug tested. If those rules are not followed, a doctor can face sanctions or restrictions to his medical license."
Suboxone was in the national news recently because the accused killer in the Charleston, S.C., shootings was arrested for illegal possession of it four months ago at a South Carolina shopping mall, the Herald-Leader notes.
The drug is buprenorphine, the active ingredient in the brand-name drugs Suboxone and Subutex, which became more popular in 2012, when the state cracked down on "pill mills" that were freely handing out prescriptions for painkillers. "A lot of the pill mills morphed into facilities that dispense these prescriptions," Dr. John Langefeld, medical director for the state's Medicaid program, told Meehan.
Also, Meehan writes, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act required insurance plans to cover treatment for substance abuse, and "as more Medicaid patients and others got health-insurance coverage, more people obtained prescriptions for buprenorphine, Langefeld said. . . . According to a state report, one user obtained prescriptions from nine doctors."
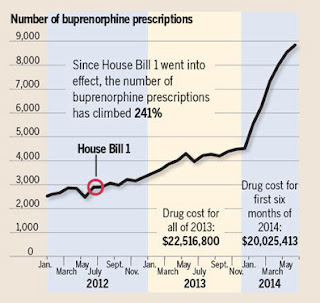 |
| Lexington Herald-Leader chart by Chris Ware from state data |
Suboxone is supposed to be taken in conjunction with therapy and drug testing. "a patient receives a controlled dose of a legal drug as the dose is tapered by a physician for a safe and effective withdrawal," Meehan notes. However, "doctors started to see Suboxone patients on a cash basis, asking for as much as $300 for an office visit that included a prescription for the maximum allowable amount of Suboxone. Patients often received no therapy or drug testing. Some patients were on the maximum dose indefinitely, Brenzel said." Some doctors prescribed the drug with other painkillers, creating an illegal market.
To prevent such abuse by unscrupulous doctors, the medical-licensure board has issued regulations that require "more physician education and the requirement that the drug be prescribed only for medically supervised withdrawal and not be given to pregnant women," Meehan writes. "Patients should also be closely monitored and drug tested. If those rules are not followed, a doctor can face sanctions or restrictions to his medical license."
Suboxone was in the national news recently because the accused killer in the Charleston, S.C., shootings was arrested for illegal possession of it four months ago at a South Carolina shopping mall, the Herald-Leader notes.

No comments:
Post a Comment